-
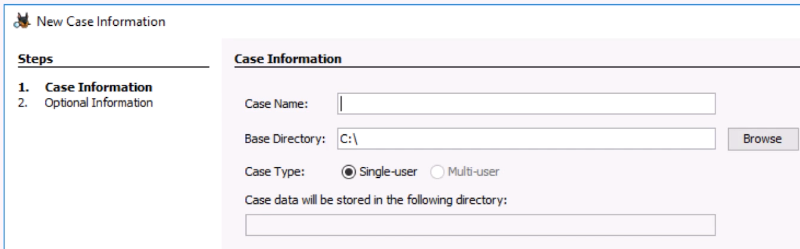
New Case Information
-
Case Name:
-
Base Directory:
-
Case Type: e.g. Single-user
-
Directory for case data
Course list http://www.c-jump.com/bcc/
Goal: overview general concepts before we make a case and start analyzing data:
Investigation Workflow
Data source
Ingest modules
Autopsy modules selected to ananyze data in a data source
Autopsy Deployment Types
single desktop user
cluster or multiuser
Central Repository

New Case Information
Case Name:
Base Directory:
Case Type: e.g. Single-user
Directory for case data
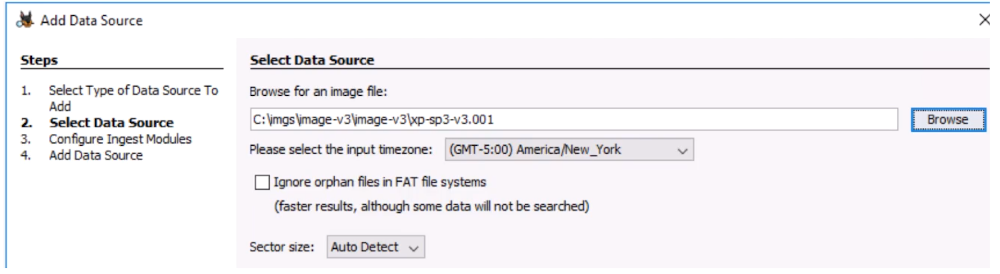
Select Data Source
Select Type of Data Source
Browse for an image file
Configure Ingest Modules
Input timezone: e.g (GMT-5:00) America/New_York
Ignore orphan files in FAT file systems (faster results, although some data will not be searched)
Sector size: Auto Detect
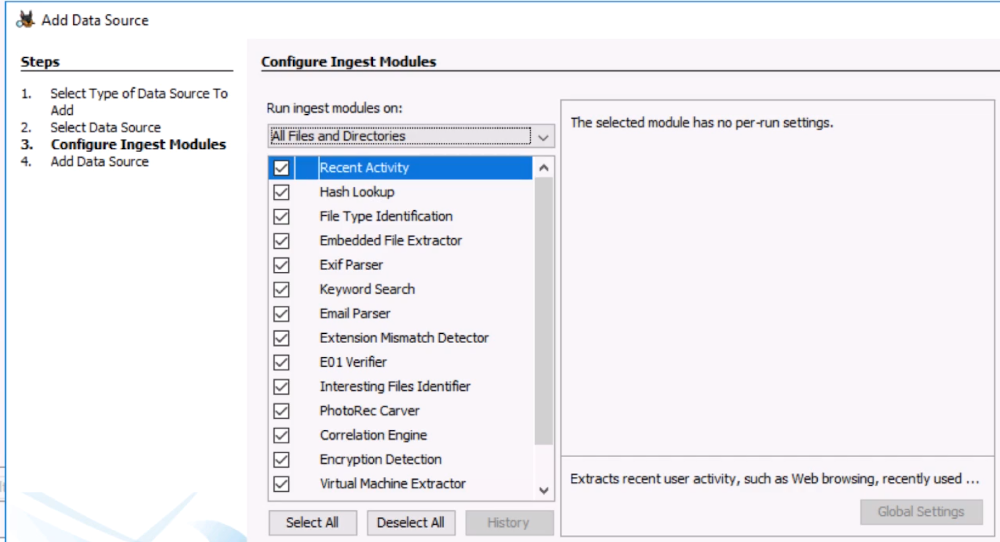
Steps to Configure Ingest Modules:
The selected module can have additional per-run settings
Run ingest modules on: All Files and Directories
Recent Activity: Extracts recent user activity, such as Web browsing, recently used
Hash Lookup
File Type Identification
Embedded File Extractor
Exif Parser
Keyword Search
Email Parser
File Extension Mismatch Detector
E01 Verifier
Interesting Files Identifier
PhotoRec Carver
Correlation Engine
Encryption Detection
Virtual Machine Extractor

Quick tags:
CAT-0: Uncategorized
CAT-1; Child Explaitation (Illegal) (Notable)
CAT-2: Child Exploitation (Non-illegal/Age Difficult) (Notable)
CAT-3; CGl/Animation (Child Exploitive) (Notable)
CAT-4; Exemplar Comparison (Interna! Use Only)
CAT-5: Non-pertinent
Evidence - Follow Up - Notable Item (Notable)
New tag... (creates custom tag)
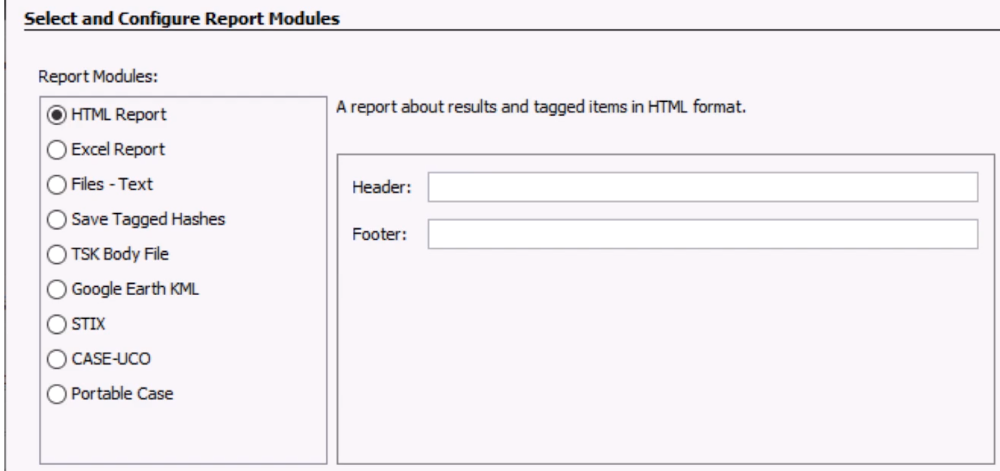
Specify Header, Footer, and select and configure Report Modules:
HTML Report: A report about results and tagged items in HTML format
Excel Report
Files - Text
Save Tagged Hashes
TSK Body File
Google Earth KML
STIX
CASE-UCO
Portable Case

Functionality:
Cases can be opened by only one person at a time
Similar approach to nearly every other forensics tool
Technical aspects:
Everything runs on a single computer
Works out of the box with a simple installer
Launching Autopsy will start all embedded services (database, text indexing, etc.)
Functionality:
Cases can be opened by multiple users at the same time
Allows for Auto Ingest mode where new media is automatically analyzed 24x7 by multiple nodes
Faster analysis because database is often faster
Technical aspects:
User experience is the exact same
Uses central servers for database, text index, etc.
Uses central high speed storage
Database that stores data from past cases:
MDS Hash values
Comments
Wifi SSIDs
...
Why is it needed?
Allows you to easily access important data from past cases
Autopsy typically has case-specific databases
Keeps databases smaller and easier to manage
Allows for archival, etc.
Examples we'll see later in our course:
"Other Occurrences" content viewer shows you if a file was seen in a past case
Comments about a file can be stored in the Central Repository and shown when file is seen again in the future.
Centralize management of notable hash sets
Automatically flag files if they were previously tagged as notable
Two types are supported:
SQLite:
Requires no other installations
Can be used by only one user at a time
NOTE: Do not put on a network share and have multiple examiners using it at the same time. Concurrent access is not supported.
PostgreSQL
Database is stored on a server
Can be used by multiple users at a time
Can use the same server for multi-user cases.
If you are a single-person shop, stick with SQLite
If there are multiple people in your lab, setup PostgreSQL
It's fairly easy
Follow the instructions in the Autopsy User documentation